According to Ayurveda Chief Constituents of Body
Chief Constituents of the body According to Ayurveda
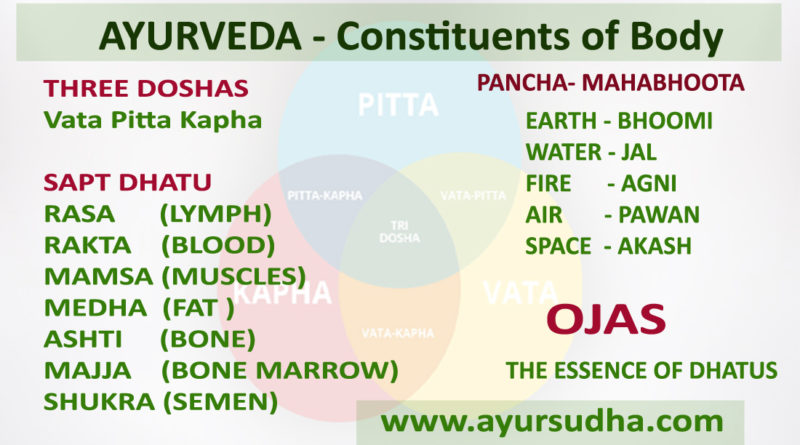
Dosha : Vata, Pitta and Kapha
Dhatu : Body tissues – Rasa (lymph / product of digestion), Rakta (blood), Mamsa (muscle), Meda (fat), Asthi (bone), Majja (bone marrow) and Shukra (male and female reproductory secretions)
Mala : waste products : sweat, urine and faeces Doshas, are the roots of the body.
Functions of Vata Dosha – Vata Dosha Karma :
Vata is responsible for all movements. (Movement of blood in blood vessels, movement of nutrients, movement of air in lungs, locomotion. In its normal state Vata causes enthusiasm.
Vatha Dosha regulates respiration process
Regulates all loco-motor movements
Regulates all activities of mind
speech
initiation of natural urges (tears, faeces, urination, sneezing, coughing, vomiting yawning etc) maintenance of the Dhatus (tissues) in their normalcy and proper functioning of the sense organs.n movements of hands and legs etc. )
Functions of Pitta Dosha – Pitta Dosha Karma:
In its normal state Pitta causes digestion and metabolism
Maintenance of body temperature.
vision
Causes hunger, thirst, appetite.
Maintains skin complexion, intelligence, courage, valour, and softness (suppleness) of the body.
Functions of Kapha Dosha -Kapha Dosha Karma:
Kapha confers stability, lubrication, compactness (firmness) of the joints.
Kshama : It is the cause for mental capacity to withstand or withhold emotions, strains etc. It is also cause for forgiveness
Functions of body tissues and waste products – Prakrita Dhatu Mala Karma :
Functions of body tissues – Dhatu Karma :
Rasa Dhatu (product of digestion and metabolism) : provides nourishment
Rakta (blood) : maintenance of life activities
Mamsa (muscle): it covers around bones and enables voluntary and involuntary actions
Meda (fat) :lubrication
Asthi (bones): support, forms the framework of the body
Majja (bone marrow):filling the inside of the bones and
Shukra (male and female reproduction system):conception and pregnancy.
Functions of waste products – Mala Karma:
Maintenance of strength of the body is the chief function of faeces.
Elimination of moisture (water) is of urine.
Slow elimination of moisture is of the sweat.
Effects of increased Vata – Vata Vruddhi Lakshana:
Vata: when increased produces
Karshya : emaciation
Karshnya : black discoloration
Ushnakamitva:desire for hot things
Kampa : tremors
Anaha : bloating, fullness, distention of the abdomen
Shakrut Graha : constipation
Bala bhramsha: loss of strength
Nidra bhramsha : loss of sleep
Indriya bhramsha :loss of sensory functions
Pralapa :irrelevant speech
Bhrama :Delusion, Dizziness giddiness
Deenata : timidity (peevishness).
Effects of increase of Pitta – Pitta Vruddhi Lakshana :
Pitta when increased produces yellow discoloration of the faeces, urine, eyes, and skin.
excess of hunger and thirst
feeling of burning sensation and
very little sleep.
Effects of increased of Kapha – Kapha Vruddhi Lakshana :
Kapha, when increased produces
Agnisadana :weak digestive activity
Praseka : excess salivation
Alasya :lassitude, laziness
Gaurava :feeling of heaviness
Shvaithya : white discoloration
Shaithya :coldness
Shlathangatva : looseness of the body parts
Shwasa : dyspnoea, asthma, COPD
Kasa: cough, cold
Atinidrata :excess of sleep.
Effects of increased body tissues – Vriddha Dhatu Karma:-
Rasa when increased in similar to Kapha, produces the same symptoms of increased Kapha.
Rakta Dhatu Vruddhi Lakshana :
Blood tissue, when increased produces
Visarpa : Herpes, spreading skin disease
Pleeha :diseases of the spleen
Vidradhi : abscesses
Kushta :skin diseases
Vatasra : gout
Pittasra : bleeding disease
Gulma : abdominal tumors
Upakusa :a disease of the teeth
Kamala :jaundice
Vyanga : discolored patch on the face
Agninasha : loss of digestion strength
Sammoha :Coma, unconsciousness
Red discoloration of the skin, eyes, and urine.
Mamsa Dhatu Vruddhi Lakshana:
Muscle tissue, when increased produces
Ganda :cervical lymphadenitis
Granthi: tumor
Increase in size of the cheeks, thighs, and abdomen
over growth of muscles of the neck and other places.
Medo Dhatu Vruddhi Lakshana:
Fat tissue), when produces similar symptoms and in addition, it causes fatigue, difficulty in breathing even after little work,
drooping of the buttocks, breasts and abdomen.
Asthi Dhatu Vruddhi Lakshana:
Bone tissues, when increased causes overgrowth of bones and extra teeth
Majja Dhatu Vruddhi Lakshana:
BoneMarrow, when increased produces heaviness of the eyes and the body, increase of size of the body joints and causes ulcers which are difficult to cure.
Shukra Dhatu Vruddhi Lakshana :
Reproductive tissue, when increased produces great desire for the woman (sexual desire) and seminal calculi (spermolith).
Effects of increased waste products – Vriddha Mala Karma:
Puresh (feaces), when increased causes distension of abdomen, gurgling noise and feeling of heaviness.
Mutra (urine), when increased produces severe pain in the bladder and feeling of non-elimination even after urination.
Sweda (sweat) when increased produces excess of perspiration, foul smell and itching.
Functions decreased Doshas – Ksheena Doshakarma:
Vata Kshaya Lakshana:
Decreased Vata produces symptoms like:
Angasada: debility of the body
Alpa bhashite hitam: the person speaks very little
Sanjna moha: loss of sensation (awareness) and of consciousness and
occurrence of all the symptoms of increased Kapha.
Pitta Kshaya Lakshana:
Decreased Pitta causes
Mande anala : weakness of digestive activity
Shaitya :coldness
Prabha hani :loss of luster (complexion).
Kapha Kshaya Lakshana:
Decrease of Kapha causes
Bhrama : Delusion, Dizziness
Shunyatva: emptiness of the organs of Kapha
hrudrava :tremors of the heart (palpitation)
Shlatha sandhita: looseness of the joints.
Symptoms of decrease of Dhatu (body tissues) :
Decrease of Rasa dhatu produces dryness, fatigue, emaciation, exhaustion without any work andnoise intolerance.
Decrease of Rakta produces desire for sour and cold things, loss of tension of veins (and arteries) and dryness.
Decrease of Mamsa causes debility of the sense organs, emaciation of cheeks, buttocks and pain in the joints.
Decrease of Medas causes loss of sensation in the waist, enlargement of spleen and emaciation of the body.
Decrease of Asthi causes pain in the joints, falling off of the teeth, hairs, nails etc.
Decrease of Majja causes hollowness (of the bones inside) giddiness and seeing of darkness
Decrease of Shukra results in delay in ejaculation, ejaculation accompanied with bleeding, severe pain in the testicles and a feeling of hot fumes coming out of the urethra.
Symptoms of decreased waste products :
Decrease of faeces gives rise to gurgling noise in the intestines and bloating, vata moves in upward direction in the intestine causing discomfort and pain in the region of the heart and flanks.
Decrease of urine causes scanty urination, dysuria, urine discoloration or hematuria.
Decrease of sweat leads to falling of hair, stiffness of hair and cracking of the skin.
Decrease of Malas which are of little quantity is difficult to perceive, it should be inferred from the dryness, pricking pain, emptiness and tightness of their sites of production and elimination.
The decrease of Dosha Dhatu etc can be observed by the increase of opposite qualities.
The increase of Dosha Dhatu etc can be observed by the increase of similar qualities.
The increase of Malas is observed by their non-elimination (too much of waste product accumulation leading to obstruction) and their decrease by too much of elimination
Body being acustomed to accumulation of waste products (in intestines and bladder), the decrease of waste product formation is more troublesome than their increase.
Relationship between Dosha and Dhatu:
Vata resides in Asthi (bones)
Pitta resides in Sweda (sweat) and Rakta (blood)
Kapha resides in rest of the Dhatu and Mala.
In case of Pitta and Kapha, when there is an increase of Pitta or Kapha, there is also respective increase of tissues and waste products associated with them.
For example, if Pitta increases, then sweat and blood vitiation also increases. The same rule applies to decrease as well.
But in case of Vata, if Vata decreases, then Asthi increases. They are inverse proportionately related with each other.
Cause for increase or decrease of Dosha:
The increase of Doshas, Dhatus and Mala is usually due to excess nutrition (Tarpana), which is followed later on with increase of Kapha.
Whereas the decrease of Doshas, Dhatus and Malas is due to loss of nutrition which is followed, later with increase of Vayu (Vata).
Hence, the diseases arising from increase of Dosha and Dhatu should be usually treated quick by adopting Langhana (therapy causing thinning of the body, reducing the quantity)
The diseases arising from the decrease of Dosha and Dhatu should be treated with Brimhana therapy (causing stoutening the body, increasing the quantity etc.)
But in case of Vata, the order is reverse. If Vata is increased, then Brihmana therapy (nourishing therapy) should be adopted and if Vata decreases then Langhana therapy should be adopted.
Effects of vitiated Doshas – Dusta Dosha Karma :
Two below : anus and urethra,
seven in the head and
the channels of sweat; from these vitiated channels develop their connected The Doshas which are vitiated (become abnormal undergoing either increase or decrease)cause vitiation of the Rasa and other Dhatus (tissues) next
Both Doshas and Dhatus togeter vitiate the Malas (waste products) which in turn, vitiate the Malayanas (channels of their elimination).
Malayana – routes of elimination of waste products are –
diseases.
Ojas – the essence of Dhatus :
Ojas is the essence of the Dhatus;
It is mainly located in the heart. It is present all over the body and regulates health.
Qualities :
Snigdha :unctuous, oily
Somatmaka : watery
Shuddha : clear (transparent),
Ishat Lohita Peetakam : slight reddish yellow in colour;
Loss of Ojus leads to loss of life.
All aspects of health are related to Ojas.
Cause for decrease of Ojas:
Ojas undergoes decrease in quantity by anger, hunger (starvation), worry, grief, exertion etc.
Symptoms of Ojas decrease :
The person becomes fretful, debilitated, repeatedly worries without any reason, feels discomfort in sense organs, develops bad complexion, negative thoughts and dryness.
Treatment – Use of drugs of Jivaniya group (Enlivening) in milk, meat juice etc.
Notes :- Many more causes of decrease of Ojas have been mentioned in other texts of Ayurdeva, they are
Ativyayama :too much exercise
Anashana : fasting for long periods of time
Alpasana :eating less quantities of food
Rooksapana:(intake of alcoholic beverages which cause dryness)
Pramitasana :(intake of mixture of good and bad foods)
Bhaya (fear)
Prajagara (waking up at night)
Abhighata (injury)
Abhishanga (assault by evil spirits; micro organisms like bacteria, virus etc.), Dhatukshaya (depletion of tissues such as by haemorrhage etc.)
Ativisarga (too much of elimination) of Kapha, Sonita (blood), Sukra (semen) and Mala (waste products)
Visha (ingestion of poison)
Increase of Ojas makes for contentment, nourishment of the body and increase of strength.
The increase of Doshas should be controlled by avoidance of foods which are disliked.
The decrease of Doshas should be managed by foods indulgence of food that are desired.
The Doshas which have undergone increase and decrease generally produce desire for foods which are dissimilar and similar (in properties to those of the Doshas) respective, but the unintelligent person do not recognize them.
The Doshas, when increased produce their respective features (signs and symptoms) depending upon their strength; when decreased they do not produce signs and symptoms and when normal, they attend to their normal functions.
The very same Doshas, which when normal, are the causes for growth of the body, become the causes for its destruction when abnormal.
Hence by adopting suitable measures, the body should be protected from their decrease and increase
At Ayur-Sudha – Ayurvedic Treatments in Punjab, India. Our team of Ayurvedic Doctors take proper analysis of dosha of body and then start treatment of all chronic diseases. Psoriasis treatment, Lichen Planus treatment, Vitiligo Treatment, Acne treatment, Eczema treatment, Pemphigus Vulgaris treatment with Ayurvedic medicines. Many patients visits our Ayur- Sudha Ayurvedic Centre Jalandhar, Punjab from different states Haryana, New Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu, Noida, Chandigarh, Gujrat, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh , Mumbai and other states for Skin Treatments in Ayurveda.
AYUR-SUDHA
Ayurvedic Treatment for Skin Diseases in Punjab, India
Best Ayurvedic Centre in Jalandhar, India
Ayurveda Clinic.